One of the most pressing questions for techies who are new to Oracle is How to check oracle version of database be it Windows, Solaris or Linux there are commands which can be executed with right permission to get the version details.
So let’s start, Prerequisite is that you should be able to login to the instance.
Table of Contents
How to check oracle version in Linux
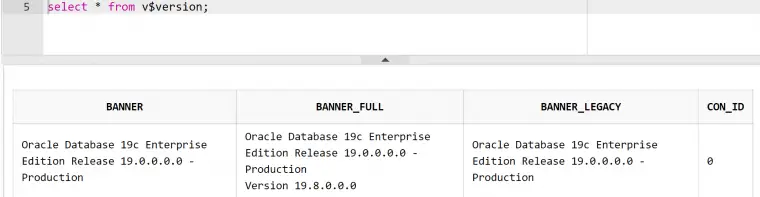
Use Command on SQL Plus
select * from v$version;
How to find client sqlplus version in use
sqlplus -v SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
How to Oracle Database version in SQL developer
How to check Oracle Database version in SQL developer
Total Time: 2 minutes
Connect to Database in SQL Developer
In SQL Developer, click the Reports tab on the left, near the Connections navigator.
Launch Reports Navigator
In the Reports navigator, expand Data Dictionary Reports.
Check Data Dictionary Reports
Under Data Dictionary Reports, expand About Your Database.
Click About Your Database
Under About Your Database, click Version Banner.
The Oracle database server is available in the following editions:
Oracle Enterprise Edition
Oracle’s top-end database server product for big enterprise customers.
Oracle Standard Edition
Four-processor version of Oracle Database, including full clustering support (Real Application Clusters).
Oracle Standard Edition One
Two-processor version of Standard Edition at an attractive entry-level price. While Real Application Clusters is included in the installation package, the right to use is NOT included with Standard Edition One.
Oracle Personal Edition
Full-featured version for individuals, compatible with the entire Oracle Database family (except Real Application Clusters).
Oracle Express Edition
Free version of Oracle that is limited to 1 processor, 1 GB RAM and 11 GB of data. For more info, see Oracle XE.
Oracle Database Versions
Oracle has released various versions of the Oracle database starting in 1979. They release Oracle 8i in 1998 where “i” stand for the internet. They release Oracle 10g in 2003 where “g” stands for grid. Then they release Oracle 12c in 2013 where “c” stands for the cloud. After that, they continued year-wise starting in 2018. So 2018 was 18c Release, 2019 was 19c Release, and so on.
The latest Innovation release of Oracle Database 21c, the world’s most popular database, is now generally available “cloud first” in the Oracle Cloud Database Service Virtual Machine (for RAC and single instance) and Bare Metal Service (single instance). It’s also available in the Oracle Autonomous Database Free Tier Service in Ashburn (IAD), Phoenix (PHX), Frankfurt (FRA), and London (LHR) regions. General availability of Oracle Database 21c for on-premises platforms, (including Oracle Exadata, Linux, and Windows) will follow in 2021.
Oracle Release Versions
TOP Features according to Version of Oracle database from the first version are as follows.
| Version & Year | New Features |
| Oracle v2, 1979 | First commercially SQL-based RDBMS |
| Oracle v3, 1983 | Concurrency control, data distribution, scalability |
| Oracle v4, 1984 | Multiversion read consistency |
| Oracle v5, 1985 | Client/server computing Support & distributed database systems |
| Oracle v6, 1988 | Row-level locking, scalability, online backup and recovery, PL/SQL, Oracle Parallel Server |
| Oracle 7, 1992 | PL/SQL stored procedures, Triggers, Shared Cursors, Cost Based Optimizer, Transparent Application Failover |
| Oracle 8, 1997 | Recovery Manager, Partitioning, Dataguard, Native internet protocols, Java, Virtual Private Database |
| Oracle 9, 2001 | Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC), Oracle XML DB, Data Mining, Streams, Logical Standby |
| Oracle 10gR1, 2003 | Grid infrastructure, Oracle ASM, Flashback Database, Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor |
| Oracle 10gR2, 2005 | Real Application Testing, Database Vault, Online Indexing, Advanced Compression, Transparent Data Encryption |
| Oracle 11gR1, 2007 | Active Data Guard, Secure Files, Exadata |
| Oracle 11gR2, 2009 | Data Redaction, Hybrid Columnar Compression, Cluster File System, Golden Gate Replication, Database Appliance |
| Oracle 12cR1, 2013 | Multitenant architecture, In-Memory Column Store, Native JSON, SQL Pattern Matching, Database Cloud Service |
| Oracle 12cR2, 2016 | Native Sharding, Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance, Exadata Cloud Service, Cloud at Customer |
| Oracle 18c, 2018 | Autonomous Database, Data Guard Multi-Instance Redo Apply, Polymorphic Table Functions, Active Directory Integration |
| Oracle 19c, 2019 | Automatic Indexing, Data-guard DML Redirect,Partitioned Hybrid Tables, Real-time Stats + Stats Only Queries |
| Oracle Database 21c 2021 | “cloud first” in the Oracle Cloud Database Service Virtual Machine (for RAC and single instance) and Bare Metal Service (single instance) |
Oracle database release version nomenclature
| Major Database Release Number | The first digit is the most general identifier. It represents a major new version of the software that contains significant new functionality. |
| Database Maintenance Release Number | The second digit represents a maintenance release level. Some new features may also be included. |
| Application Server Release Number | The third digit reflects the release level of the Oracle Application Server (OracleAS). |
| Component-Specific Release Number | The fourth digit identifies a release level specific to a component. Different components can have different numbers in this position depending upon, for example, component patch sets or interim releases. |
| Platform-Specific Release Number | The fifth digit identifies a platform-specific release. Usually, this is a patch set. When different platforms require the equivalent patch set, this digit will be the same across the affected platforms. |
[content-egg module=Udemy]
FAQs
What is current Oracle version?
Oracle Version 21 C
What is the release version nomenclature
Beginning in 2018, a new numbering schema for the database software is implemented. Instead of a legacy nomenclature such as 12.2.0.2, a three (3) field format consisting of: Year.Update.Revision is used, such as 18.1.0. This allows clear indication of:
the feature release designation of the database software (the first field)
the quarterly Update (the second field)
the quarterly Revision (the third field)
How many Revisions are going to be released per Update?
Each Update is followed by up to two, separate, quarterly, revisions for the six months after the Update is released. Remember that Revisions are only provided for Long Term Releases
How to get a direct root access to DBCS classic instance?
Oracle doesn’t allow direct access to root on cloud machines. sudo is the only option users have to access the root privileges.
There is a alternative way of achieving this doing below, Refer MOS note Doc ID 2507383.1
more oracle