SQL where contains is used to check the value if present in a column. Mostly used in Unstructured data testing on text based fields.
In oracle, the column where we need to apply contains needs to be indexed.
In SQL Server CONTAINS is a predicate used in the WHERE clause of a Transact-SQL SELECT statement to do a full-text search on full-text indexed columns containing character-based data types. Note that indexing is required on the column.
In SQL Server the syntax is
In Oracle the column needs to be indexed to use the contains clause
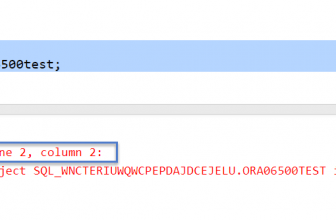
If the column is not indexed you will receive an error:
- ORA-20000: Oracle Text error:
- DRG-10599: column is not indexed
SQL Contains String Examples :
The requirement to search inside a string can be achieved by
1. Using LIKE Operator
When we need to search a string for a value we can use the LIKE operator
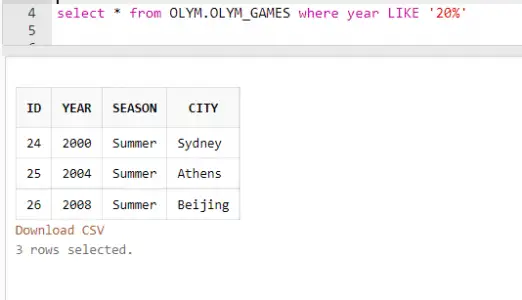
e.g select * from OLYM.OLYM_GAMES where year LIKE ‘20%’
In this SQL query we want to find the games which are happening in 21st century.
2: Using INSTR Operator :
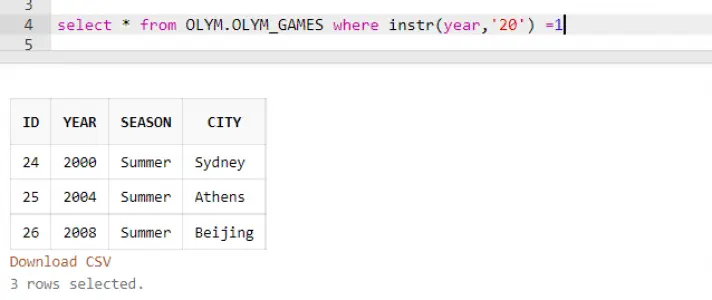
We can do the same using the INSTR Operator as well
select * from OLYM.OLYM_GAMES where instr(year,’20’) =1
3. In SQL Server if the same table was there the SQL would be like
Select * from OLYM.OLYM_GAMES where CONTAINS(Year,’20’);
See also :